The System Unit
Electronic Data and Instructions
• Data and instructions are represented electronically
• Two-state system or Binary System
– Off/on electrical states
– Characters represented by 0s (off) and 1s (on)
– Bits
– Bytes
Character Coding Schemes
• Three types of binary coding schemes
– ASCII - American Standard Code for Information Exchange
– EBCDIC - Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code
– Unicode – handles languages with large numbers of characters
System Board
• Connects all components
• Allows communication between devices
• Main board or motherboard
• Circuit board electronic components
– Sockets
– Slots
– Bus lines
Microprocessor Chips
• Central Processing Unit (CPU)
• Two Basic Components
– Control unit
– Arithmetic-logic unit (ALU)
• Chip capacities are expressed in word sizes
• Two Recent Significant Developments
– 64-bit processors
• Have become standard for most of today’s desktop and laptop computers
– Multi-Core Chips
• Can provide two
separate and
independent CPUs
separate and
independent CPUs
• Parallel processing
Specialty Processors
• Coprocessors
– Designed to improve specific computing operations
– Graphics coprocessors
• Smart cards
– Credit card sized with an embedded chip
– Used by many universities
• Specialty processors in cars
– As many as 70
– Used to control features
• RFID tags
– Information chips
– Used for tracking purposes
Memory
- Holding area for data, instructions, and information
- Memory is contained on chips connected to the system board
- Types of memory chips
- RAM
- ROM
- Flash
RAM
• Random Access Memory (RAM) chips hold the program and data
– Cache memory or RAM cache
– Flash RAM or flash memory
• Other types of RAM
– DRAM
– SDRAM
– DDR
– Direct RDRAM
ROM
• Read-only memory (ROM) chips are not volatile and cannot be changed by the user
• CPU can read, or retrieve data and programs but the computer cannot write
• Contain special instructions
– Needed to start a computer
– Give keyboard keys their special capabilities
– Put characters on screen
Flash
• Flash memory offers a combination of the features of RAM and ROM.
• Flash memory is used for a wide of range of applications.
• If changes are made to the computer system, these changes are reflected in flash memory.
Expansion Slots and Cards
• Allow for new devices to be added
– Open architecture
– Slots provide for expansion
• Expansion cards are also called …
– Plug-in boards
– Controller cards
– Adapter cards
– Interface cards
Commonly Used Expansion Cards
TV Tuner Cards And Video Clips
• Allows you to view your favorite TV shows while running other applications such as Excel
• Video can be captured to a file, added to a Web page, attached to an email, or added to a class presentation
• Relatively inexpensive
and easy to install
and easy to install
Plug and Play
• Set of specific hardware and software standards developed by Intel, Microsoft, and others
• Creating devices that are able to configure themselves when installed
Bus Lines
• Connect parts of the CPU to each other
• Data roadway for traveling bits
– Measured as bus width
– More lanes, faster traffic
• Two basic categories
– System buses
– Expansion buses
Expansion Buses
• Connects the CPU to other components on the system board, including expansion slots
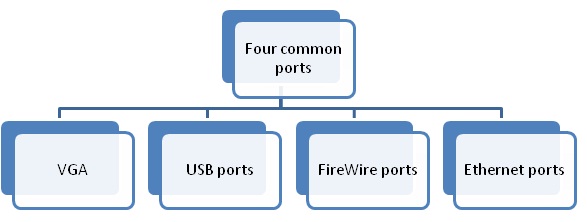
Ports
• Socket for connecting external devices
• Ports can connect directly to the system board or they can connect to cards that are inserted into slots on the system board
• Three Types
– Standard Ports
– Legacy Ports
– Specialized Ports
Legacy Ports
Specialized Ports
• Three specialized ports
– Musical Instrument digital interface (MIDI)
– Sony/Philips Digital Interconnect Format (S/PDIF)
– High Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI)
Power Supply
• Computers require direct current (DC)
• DC power provided by converting alternating current (AC) from wall outlets or batteries
• Desktop computers use power supply units
• Notebooks and handhelds use AC adapters
Careers In IT
• Computer technicians repair and install computer components and systems
• Employers look for
– Certification in computer repair
– Good communication skills
• Continued education is
required
required
• Computer technicians can
expect to earn an hourly
wage of $13.50 to $22.50
expect to earn an hourly
wage of $13.50 to $22.50
A Look to the Future
• Wearable computers
• Send and receive email while jogging
• Maintain your personal schedule book
• Remember the names of people at a party
Standard Ports






0 Response to "The System Unit"
Post a Comment